Next level drone control with just swipe of fingers. Researchers from China performs video demonstration
November 11, 2024 at 4:00 PM
3 minutes read

Chinese researchers have unveiled a breakthrough in drone control technology: a wearable touchpad that allows users to command drones with a simple swipe of their fingers. This innovation, developed by a team from Northeastern University in China, could revolutionize how humans interact with machines.
The wearable touchpad enables seamless control through intuitive swipe gestures. The device captures swipe patterns and transmits them via Bluetooth to a drone control platform, which then relays the commands to the drone. Tian Ye, an associate professor at Northeastern University, emphasized the potential of this technology, stating, “Amid growing demand for more compact, intelligent, and multifunctional human-machine interfaces, this high-performance touchpad marks a significant leap forward for the next generation of intelligent remote interactive platforms.”
Advanced Design and Materials
The touchpad, which resembles a Band-Aid, features a layered design that mimics the soft, flexible texture of human skin—ideal for wearable devices. The base layer is made of Ecoflex, a soft, rubber-like material, while the middle layers consist of liquid metal electrodes and hydrogel arrays that capture touch signals. The top layer, crafted with sandpaper-like micro-surfaces, enhances sensitivity and allows the device to stretch up to 400% of its original size.
PhD candidate Liu He, the study’s lead author, explained, “The touchpad’s flexible design allows it to stretch to as much as 400 percent of its original surface area, making it versatile and suitable for a range of applications.”
Powered by Innovative Technology
At the heart of this touchpad is a self-powered sensor array based on a triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG), which requires no external power source. This TENG-based system captures the slightest swipe gestures by generating a readable voltage signal, even at minimal power consumption and cost.
To process these touch signals accurately, the research team incorporated a transformer algorithm similar to that used in AI models like ChatGPT. With adjustments, this algorithm enables the touchpad to interpret complex gestures with impressive accuracy. During tests, the touchpad achieved a 96.83% accuracy rate across six different swipe gestures, as reported in the journal Nano Energy.
Resilience in Extreme Conditions
One of the standout features of this touchpad is its ability to function in extremely cold temperatures. To overcome the limitations of traditional hydrogels, which can freeze, the team used an antifreeze ionic conductive hydrogel. This modification allows the device to retain its properties even at temperatures as low as -40°C (-40°F). Field tests confirmed the touchpad's functionality at temperatures down to -23°C.Future Applications
This study highlights the potential of integrating hydrogels and TENG technology for wearable electronics and human-machine interactions. According to Tian, this ultra-stretchable touchpad could have broad applications across various fields. “Potential uses include controlling drones in complex or extreme environments, managing IoT devices in smart homes, and enabling remote care or medical treatments,” Tian noted.
This groundbreaking technology opens up new possibilities for wearable electronics, showcasing a promising future for human-machine interaction in challenging environments.
Up next


Australian PM Albanese Criticizes Elon Musk’s Pushback on Social Media Regulations
December 1, 2024
2 minutes read

Meta Fined $428 Million in Europe Over Facebook Marketplace Antitrust Violations
November 30, 2024
2 minutes read


China’s Huawei Launches Harmony OS-Powered Mate 70 Amid Growing Global Ambitions
November 28, 2024
2 minutes read


Google and Meta Call on Australia to Delay Social Media Ban for Children
November 26, 2024
5 minutes read


TikTok CEO Reportedly Sought Elon Musk’s Advice Amid Trump Administration’s Pressure
November 24, 2024
4 minutes read


AI Chip Leader Nvidia Forecasts Fourth-Quarter Revenue Above Estimates
November 22, 2024
2 minutes read

U.S. Watchdog Finalizes Rules to Supervise Big Tech Payments and Digital Wallets
November 21, 2024
2 minutes read

Entrepreneurs Look to Start-Up Show Amid Optimism Over Easing Funding Bottlenecks
November 20, 2024
3 minutes read

Sony in Talks to Acquire Media Powerhouse Behind Elden Ring, Sources Reveal
November 19, 2024
2 minutes read

Nvidia's New AI Chips Reportedly Face Overheating Challenges in Data Centers
November 18, 2024
2 minutes read

Netflix Experiences Widespread Outage, Thousands of Users Affected in the U.S.
November 17, 2024
2 minutes read

Amazon Faces Scrutiny from House Committee Over Controversial TikTok Partnership
November 15, 2024
2 minutes read
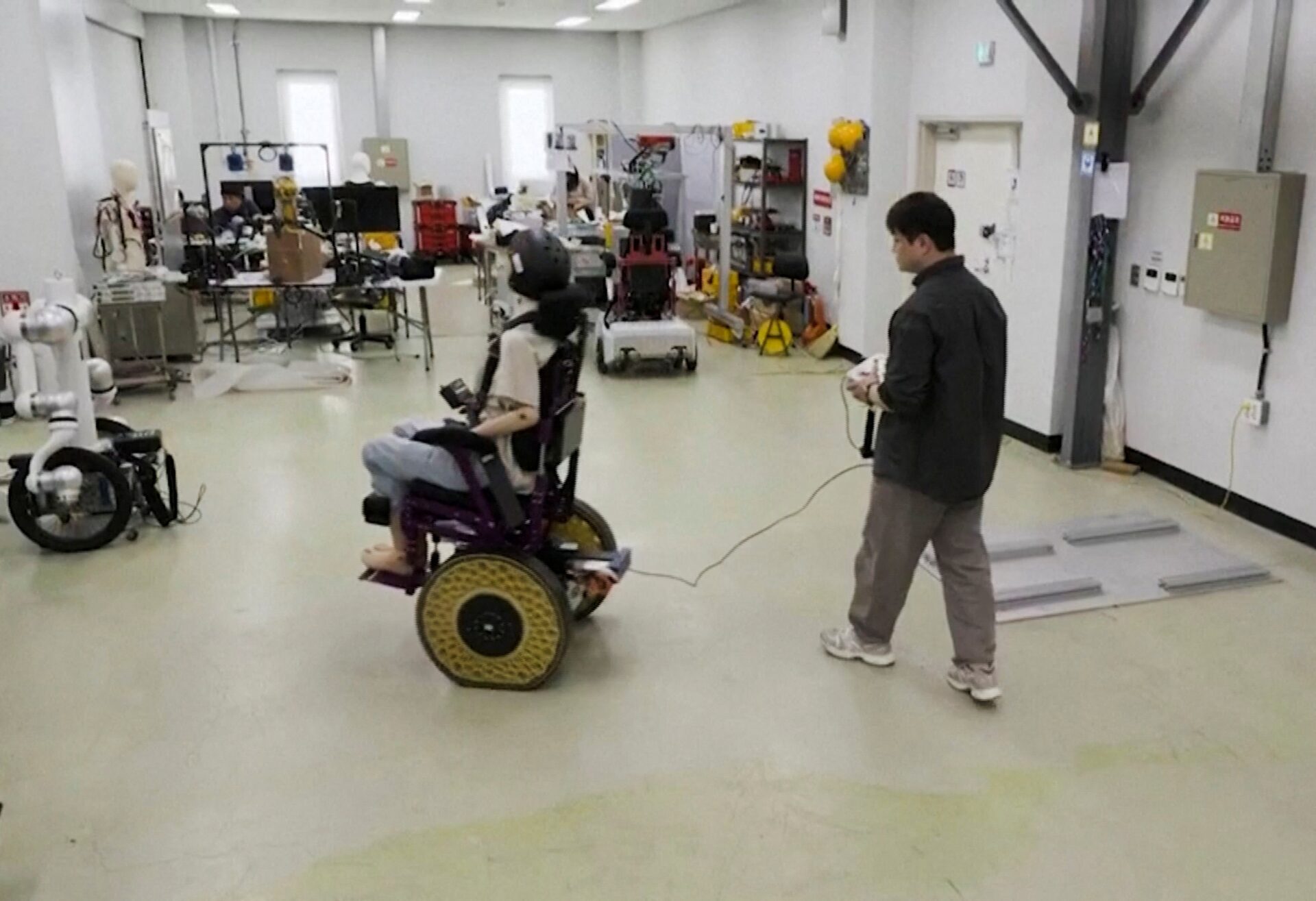

South Korean Researchers Develop 'Morphing' Wheels That Could Revolutionize Wheelchairs and Robots
November 14, 2024
2 minutes read

Microsoft President Warns the West Not to Underestimate China’s Tech Advancements
November 13, 2024
2 minutes read

SoftBank First to Receive Nvidia’s New AI Chips for Supercomputer Development
November 13, 2024
1 minute read

Unbabel CEO Predicts AI Will Replace Humans in Translation Within Three Years as It Launches New AI-Powered App
November 13, 2024
2 minutes read


Singapore’s Capital C Secures Pre-Series A Funding to Launch Super App for Southeast Asia
November 12, 2024
1 minutes read

Google and Meta Block Political Ads to Curb Misinformation, but Experts Warn It May Be Too Late
November 11, 2024
5 minutes read